sagemaker上で独自の学習モデルや予測結果を取得したいとき、 カスタムモデルを作成する必要がある
カスタムモデルの構成と変更箇所をまとめておく
環境
- python: 3.7
- gensim: 3.8.3
カスタムモデルの構成要素
AWS ECRに学習、予測用docker imageをpushすればよい
作成するカスタムモデルはword2vecで単語をベクトルを学習し、予測結果として近しい単語topnが取得できるようなもの
既存のモデルではBlazing-Textが存在するが、こちらは単語をリクエストするとその単語ベクトルを返すものだったので、今回のようなカスタムモデルを作成した
カスタムイメージの中身、実行するジョブの仕組みは以下の図のようになっている
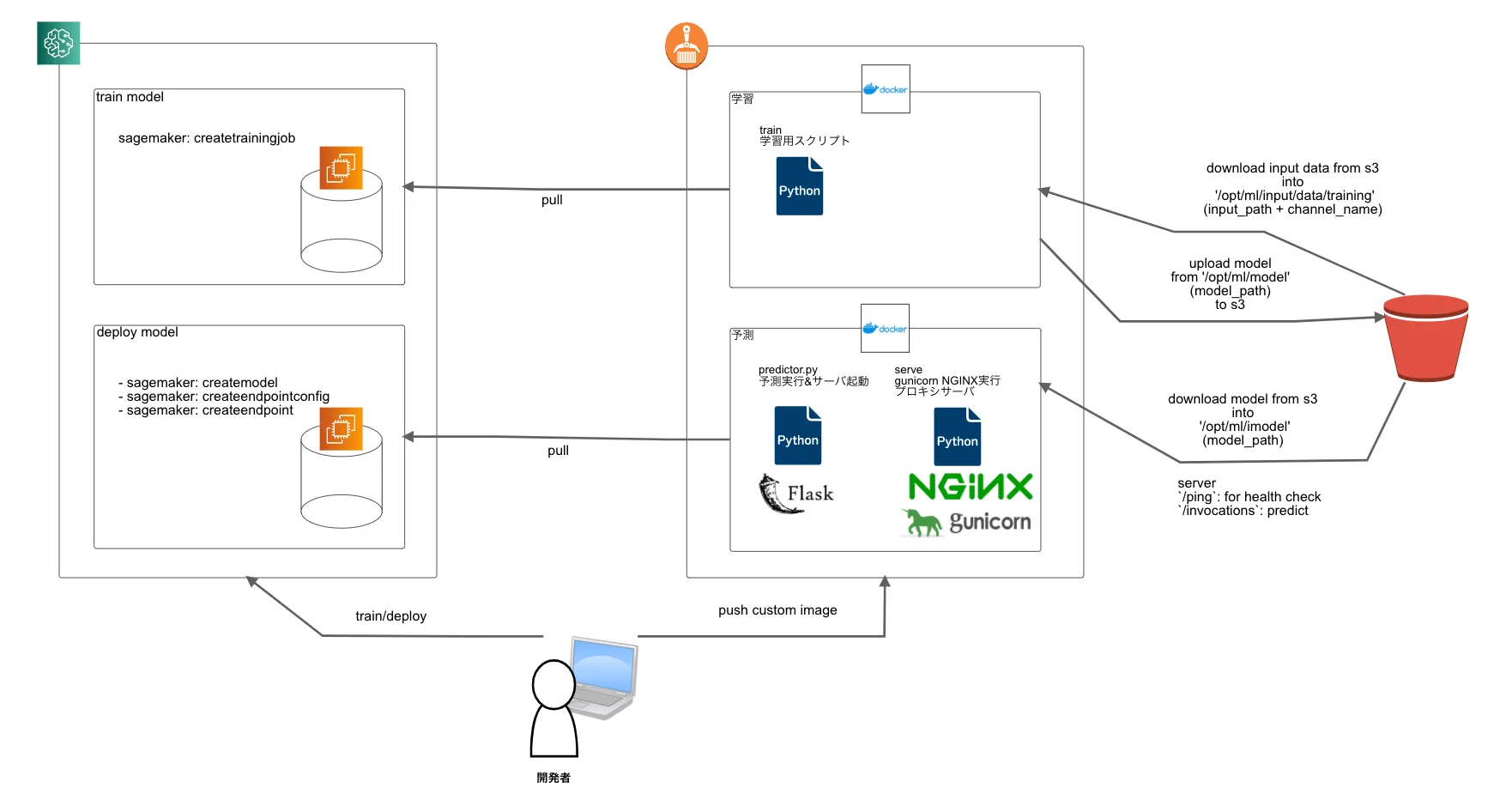
データとモデルはS3に保存され、コンテナからダウンロードされたり、アップロードされたりする
予測モデルはflaskでapiの形で提供されるが、エンドポイントが存在しないので、sdkなどを通して予測結果を取得することになる
実際のディレクトリやファイルの構成はリポジトリを参考のこと
実装
主に編集する部分である学習と予測の実行スクリプト部分の中身をのせておく
train
学習においては、学習データの格納先とモデルのアウトプット先が決まった場所になっていることに注意する
実際に学習させるときは、あらかじめデータ等をS3にuploadして、実行時に指定する
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import json
import sys
import traceback
import pandas as pd
from gensim.models import word2vec
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# These are the paths to where SageMaker mounts interesting things in your container.
prefix = '/opt/ml/'
input_path = prefix + 'input/data'
output_path = os.path.join(prefix, 'output')
model_path = os.path.join(prefix, 'model')
param_path = os.path.join(prefix, 'input/config/hyperparameters.json')
# .txt file
def load_train_data(input_dir: str) -> word2vec.PathLineSentences:
"""
Args:
input_dir(str): path of directory for train data
example for file
```
word1 word2 word3
word1 word3 word4 word5
...
```
Returns:
sentences(word2vec.PathLineSentences):
ex.)
[['word1', 'word2', 'word3'],
['word1', 'word3', 'word4'],
['word3'],
...
]
"""
sentences = word2vec.PathLineSentences(input_dir)
return sentences
# return 'False' as False
def str2bool(s: str) -> bool:
import distutils.util
return bool(distutils.util.strtobool(s))
def train_model(sentences, params, hash=hash, trim_rule=None, callbacks=()) -> word2vec.Word2Vec:
"""
refer word2vec.Word2Vec() object
Returns:
model(word2vec): word2vec object model
"""
compute_loss = params.get('compute_loss', None)
max_final_vocab = params.get('max_final_vocab', None)
max_vocab_size = params.get('max_vocab_size', None)
model = word2vec.Word2Vec(
sentences,
size=int(params.get('size', 300)),
window=int(params.get('window', 5)),
iter=int(params.get('iter', 20)),
workers=int(params.get('workers', 10)),
alpha=float(params.get('alpha', 0.025)),
batch_words=int(params.get('batch_words', 10000)),
cbow_mean=int(params.get('cbow_mean', 1)),
min_alpha=float(params.get('min_alpha', 0.0001)),
min_count=int(params.get('min_count', 5)),
null_word=int(params.get('null_word', 0)),
ns_exponent=float(params.get('ns_exponent', 0.75)),
negative=int(params.get('negative', 5)),
hs=int(params.get('hs', 0)),
sample=float(params.get('sample', 1e-3)),
seed=int(params.get('seed', 1)),
sg=int(params.get('sg', 0)),
sorted_vocab=int(params.get('sorted_vocab', 1)),
corpus_file=params.get('corpus_file', None),
max_final_vocab=max_final_vocab if max_final_vocab is None else int(max_final_vocab),
max_vocab_size=max_vocab_size if max_vocab_size is None else int(max_vocab_size),
compute_loss=compute_loss if compute_loss is None else str2bool(compute_loss),
trim_rule=trim_rule,
callbacks=callbacks,
hashfxn=hash
)
return model
# save as vectors and bin
def save_model(model, model_path):
"""
save vectors and binary model file
Args:
model(Word2Vec): gensim object
model_path(str): path for output model files
Returns:
"""
model.wv.save_word2vec_format(model_path + '/vectors.txt', binary=False)
model.save(model_path + '/model.bin')
# The function to execute the training.
def train():
print('Starting the training.')
try:
print('load train data.')
# Read in any hyperparameters that the user passed with the training job
with open(param_path, 'r') as tc:
training_params = json.load(tc)
# Take the set of files and read them all into a single pandas dataframe
# load only one file
input_files = [os.path.join(training_path, file) for file in os.listdir(training_path)]
if len(input_files) == 0:
raise ValueError(('There are no files in {}.\n' +
'This usually indicates that the channel ({}) was incorrectly specified,\n' +
'the data specification in S3 was incorrectly specified or the role specified\n' +
'does not have permission to access the data.').format(training_path, channel_name))
train_data = load_train_data(training_path)
# train
print('training...')
model = train_model(train_data, training_params)
save_model(model, model_path)
print('Training complete.')
except Exception as e:
# Write out an error file. This will be returned as the failureReason in the
# DescribeTrainingJob result.
trc = traceback.format_exc()
with open(os.path.join(output_path, 'failure'), 'w') as s:
s.write('Exception during training: ' + str(e) + '\n' + trc)
# Printing this causes the exception to be in the training job logs, as well.
print('Exception during training: ' + str(e) + '\n' + trc, file=sys.stderr)
# A non-zero exit code causes the training job to be marked as Failed.
sys.exit(255)
if __name__ == '__main__':
train()
# A zero exit code causes the job to be marked a Succeeded.
sys.exit(0)predictor.py
予測においては、モデルの読み込みパスと 定義するapiのroutingが決まったものになっていることに注意する
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import json
import sys
import signal
import traceback
try:
from StringIO import StringIO
except ImportError:
from io import StringIO
import flask
import pandas as pd
import tarfile
from gensim.models import KeyedVectors
# model file download under /opt/ml/model
prefix = '/opt/ml/'
model_path = os.path.join(prefix, 'model/')
# load model and predict
class SimilarService(object):
model = None
@classmethod
def get_model(cls):
"""
Get the model object for this instance, loading it if it's not already loaded.
"""
if cls.model is None:
# .tar.gz file
#with tarfile.open(model_path + 'model.tar.gz', 'r:gz') as tf:
# tf.extractall(path=model_path)
cls.model = KeyedVectors.load_word2vec_format(model_path+'vectors.txt', binary=False)
return cls.model
@classmethod
def predict(cls, inputs, topn=5):
"""
Args:
inputs(list): list of words for each documents. ex. ['word1', 'word2 word3',...]
topn: num of words in most_similar words.
Returns:
outputs(list): topn of similar words and scores for each words.
"""
model = cls.get_model()
outputs = []
for input in inputs:
predicts = []
try:
results = model.most_similar(positive=input.split(' '), topn=topn)
except KeyError as e:
print(e)
predicts.append({
'word': '',
'similarity': 0.0
})
outputs.append(predicts)
continue
for res in results:
word, sim = res
predicts.append({
'word': word,
'similarity': "{:.2f}".format(sim)
})
outputs.append(predicts)
return outputs
# The flask app for serving predictions
app = flask.Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/ping', methods=['GET'])
def ping():
# health check
health = SimilarService.get_model() is not None
status = 200 if health else 404
return flask.Response(response='\n', status=status, mimetype='application/json')
@app.route('/invocations', methods=['POST'])
def transformation():
data = None
# Convert from CSV to pandas
if flask.request.content_type == 'text/csv':
data = flask.request.data.decode('utf-8')
s = StringIO(data)
data = pd.read_csv(s, header=None)
else:
return flask.Response(response='This predictor only supports CSV data', status=415, mimetype='text/plain')
# check custom attributes(arg for topn)
topn = 5
try:
ca = json.loads(flask.request.headers.get('X-Amzn-SageMaker-Custom-Attributes'))
print('custom attr', ca)
topn = int(ca['topn']) if ca['topn'] is not None else 5
except Exception as e:
print('not set topn custom attribute:', e)
print('Invoked with {} records'.format(data.shape[0]))
# Do the prediction
predictions = SimilarService.predict(list(data[0].astype(str)), topn=topn)
response = {
'results': predictions
}
out = StringIO()
# return json
json.dump(response, out)
result = out.getvalue()
return flask.Response(response=result, status=200, mimetype='application/json')感想
アーキテクチャの中身を全て知らなくても、pythonとdockerを読めればなんとなくいじれるくらいのテンプレートは公開されている
作り始めは設定周りでつまづくことも多いが、 マネージドサービスなのでモデルの管理・更新が楽な面もあり、長い目で見れば実装・管理コストは低いと思った